Research Projects

Easy access to audio-visual content on social media, combined with the availability of modern tools such as Tensorflow or Keras, and open-source trained models, along with economical computing infrastructure, and the rapid evolution of deep-learning (DL) methods have heralded a new and frightening trend. Particularly, the advent of easily available and ready to use Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), have made it possible to generate deepfakes media partially or completely fabricated with the intent to deceive to disseminate disinformation and revenge porn, to perpetrate financial frauds and other hoaxes, and to disrupt government functioning. Existing surveys have mainly focused on the detection of deepfake images and videos; this paper provides a comprehensive review and detailed analysis of existing tools and machine learning (ML) based approaches for deepfake generation, and the methodologies used to detect such manipulations in both audio and video. For each category of deepfake, we discuss information related to manipulation approaches, current public datasets, and key standards for the evaluation of the performance of deepfake detection techniques, along with their results. Additionally, we also discuss open challenges and enumerate future directions to guide researchers on issues which need to be considered in order to improve the domains of both deepfake generation and detection. This work is expected to assist readers in understanding how deepfakes are created and detected, along with their current limitations and where future research may lead.
PIRCA Research Grant Awardee of PKR 45,00,000/- from Punjab HEC, 2021-2023
Other Papers: Paper
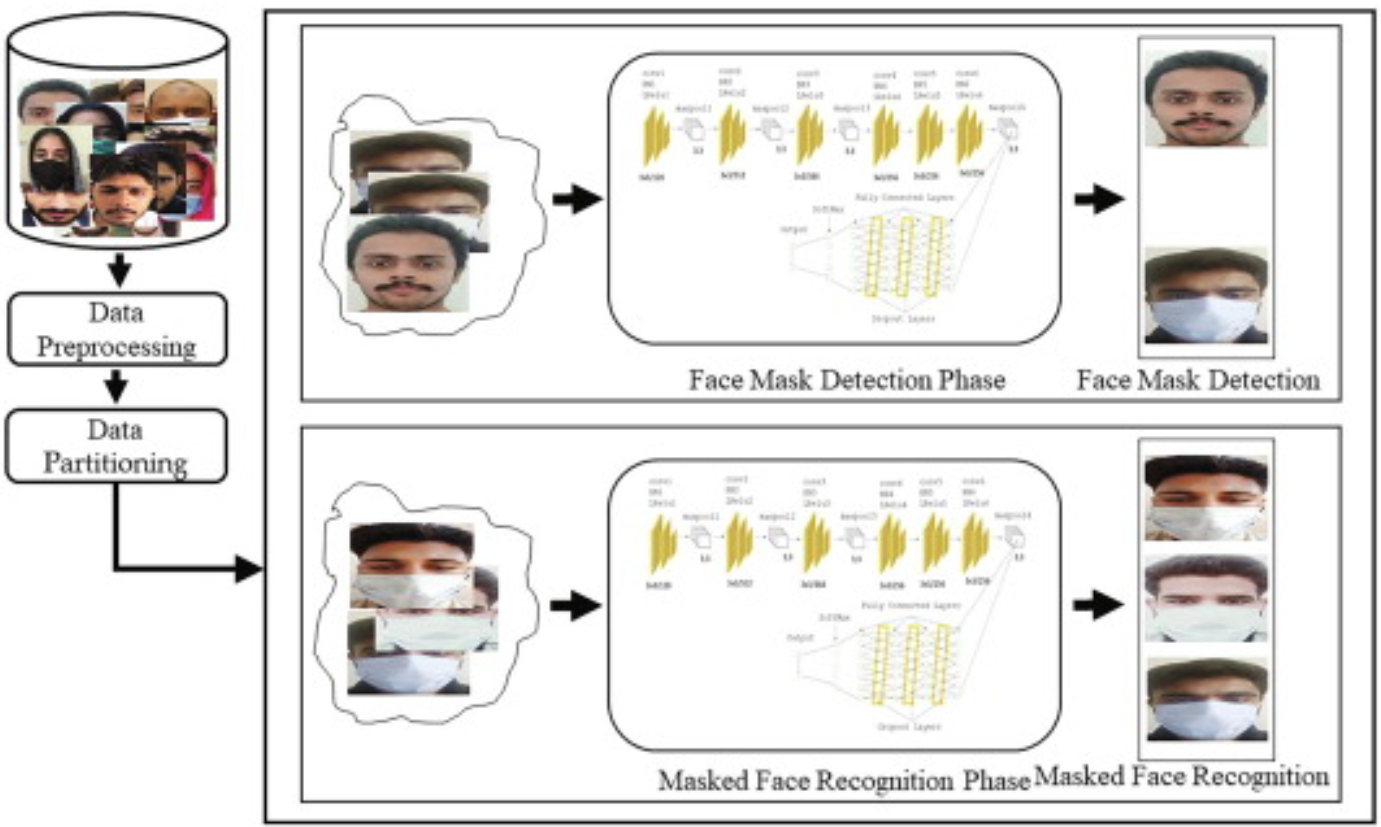
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has significantly affected the daily life activities of people globally. To prevent the spread of COVID-19, the World Health Organization has recommended the people to wear face mask in public places. Manual inspection of people for wearing face masks in public places is a challenging task. Moreover, the use of face masks makes the traditional face recognition techniques ineffective, which are typically designed for unveiled faces. Thus, introduces an urgent need to develop a robust system capable of detecting the people not wearing the face masks and recognizing different persons while wearing the face mask. In this paper, we propose a novel DeepMasknet framework capable of both the face mask detection and masked facial recognition. Moreover, presently there is an absence of a unified and diverse dataset that can be used to evaluate both the face mask detection and masked facial recognition. For this purpose, we also developed a largescale and diverse unified mask detection and masked facial recognition (MDMFR) dataset to measure the performance of both the face mask detection and masked facial recognition methods. Experimental results on multiple datasets including the cross-dataset setting show the superiority of our DeepMasknet framework over the contemporary models.
Research Grant by the Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/115), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia, 2020-2021
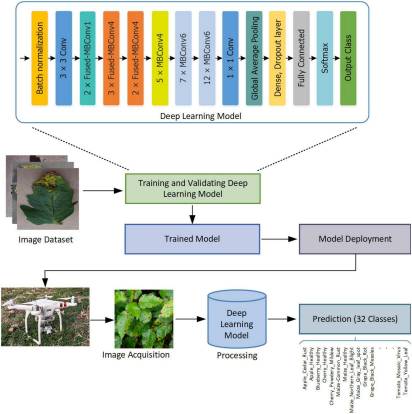
The role of agricultural development is very important in the economy of a country. However, the occurrence of several plant diseases is a major hindrance to the growth rate and quality of crops. The exact determination and categorization of crop leaf diseases is a complex and time-required activity due to the occurrence of low contrast information in the input samples. Moreover, the alterations in the size, location, structure of crop diseased portion, and existence of noise and blurriness effect in the input images further complicate the classification task. To solve the problems of existing techniques, a robust drone-based deep learning approach is proposed. More specifically, we have introduced an improved EfficientNetV2-B4 with additional added dense layers at the end of the architecture. The customized EfficientNetV2-B4 calculates the deep key points and classifies them in their related classes by utilizing an end-to-end training architecture. For performance evaluation, a standard dataset, namely, the PlantVillage Kaggle along with the samples captured using a drone is used which is complicated in the aspect of varying image samples with diverse image capturing conditions. We attained the average precision, recall, and accuracy values of 99.63, 99.93, and 99.99%, respectively. The obtained results confirm the robustness of our approach in comparison to other recent techniques and also show less time complexity.
Research Grant by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), Qassim University, Saudi Arabia, under research grant No. (10338-COC-3-1-2020-I), 2021-2022

Automated analysis of sports video summarization is challenging due to variations in cameras, replay speed, illumination conditions, editing effects, game structure, genre, etc. To address these challenges, we propose an effective video summarization framework based on shot classification and replay detection for field sports videos.
Accurate shot classification is mandatory to better structure the input video for further processing, i.e., key events or replay detection. Therefore, we present a lightweight convolutional neural network based method for shot classification. Then we analyze each shot for replay detection and specifically detect the successive batch of logo transition frames that identify the replay segments from the sports videos. For this purpose, we propose local octa-pattern features to represent video frames and train the extreme learning machine for classification as replay or non-replay frames. The proposed framework is robust to variations in cameras, replay speed, shot speed, illumination conditions, game structure, sports genre, broadcasters, logo designs and placement, frame transitions, and editing effects. The performance of our framework is evaluated on a dataset containing diverse YouTube sports videos of soccer, baseball, and cricket. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can reliably be used for shot classification and replay detection to summarize field sports videos.
Research Grant by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), University of Jeddah, Jeddah, under research grant No. (UJ-04-18-ICP), 2020-2021
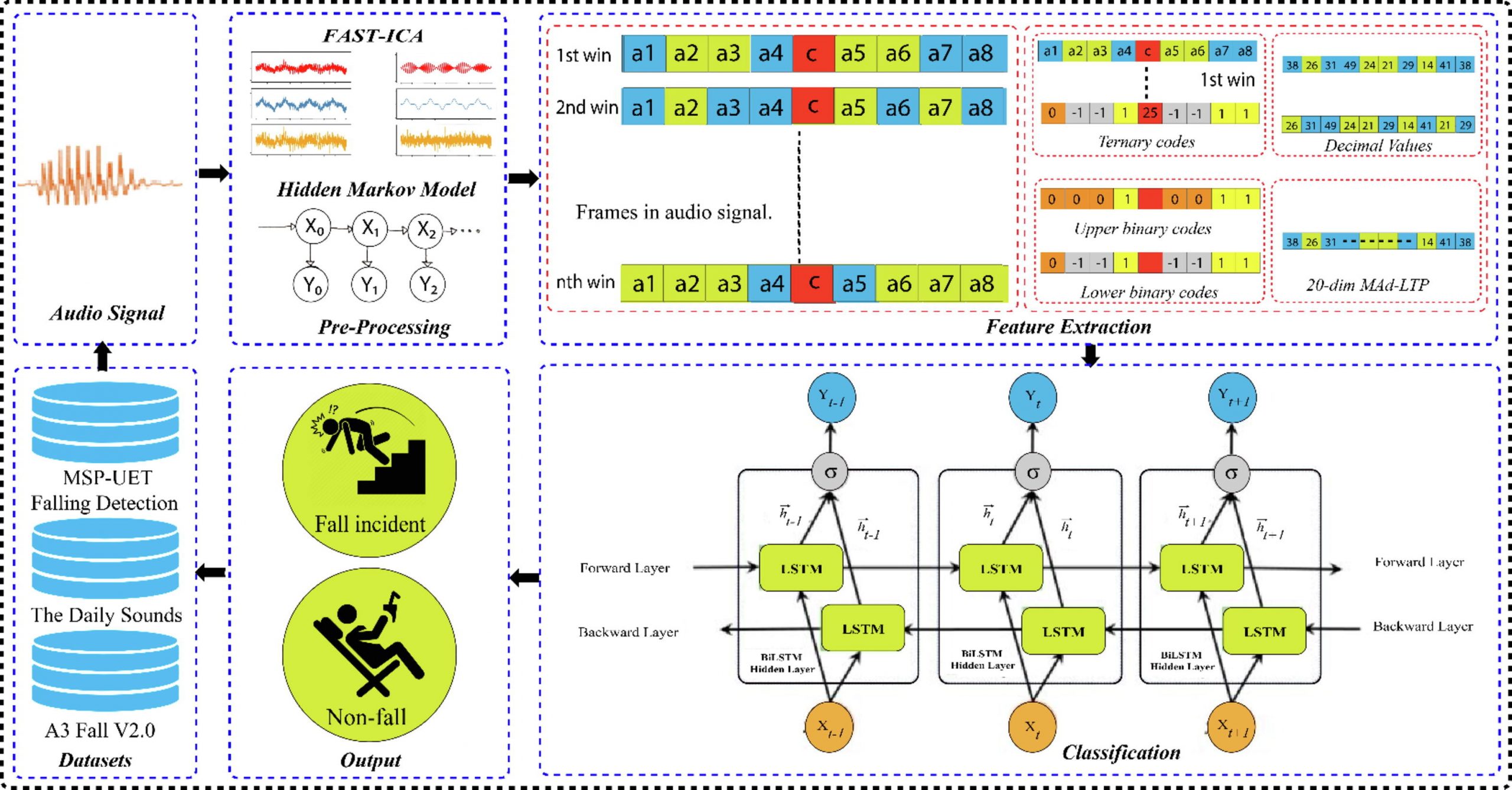
Fall detection in elder persons may result in long-lasting injury that can have severe consequences for the rest of their lives. Additionally, prolonged delay in emergency treatment after the fall event escalates the chances of mortality. Hence, fall detection at early stage is critical in terms of providing timely aid with little complications and minimize hospitalization expenses. This work aims to provide an effective and efficient healthcare solution to determine the event of fall detection for elderly persons. We aim to address this fall detection problem for elder persons living lonely and encounter issues in case they fall and are unable to call for assistance. In this paper, we present a fall detection framework by proposing a novel feature space mean absolute deviated-local ternary patterns (MAD-LTP) to examine the environmental sounds and used these features to train the BiLSTM for fall events detection. Our proposed MAD-LTP features successfully address the limitations of existing features i.e., non-robust over dynamic pattern detection, brute force optimization, intolerance over non-uniform noise, etc., for fall detection.
Research Grant by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), University of Jeddah, Jeddah, under research grant No. (UJ-20-043-DR), 2020-2021

Automated analysis of sports video summarization is challenging due to variations in cameras, replay speed, illumination conditions, editing effects, game structure, genre, etc. To address these challenges, we propose an effective video summarization framework based on shot classification and replay detection for field sports videos.
Accurate shot classification is mandatory to better structure the input video for further processing, i.e., key events or replay detection. Therefore, we present a lightweight convolutional neural network based method for shot classification. Then we analyze each shot for replay detection and specifically detect the successive batch of logo transition frames that identify the replay segments from the sports videos. For this purpose, we propose local octa-pattern features to represent video frames and train the extreme learning machine for classification as replay or non-replay frames. The proposed framework is robust to variations in cameras, replay speed, shot speed, illumination conditions, game structure, sports genre, broadcasters, logo designs and placement, frame transitions, and editing effects. The performance of our framework is evaluated on a dataset containing diverse YouTube sports videos of soccer, baseball, and cricket. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can reliably be used for shot classification and replay detection to summarize field sports videos.
Research Grant by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), University of Jeddah, Jeddah, under research grant No. (UJ-04-18-ICP), 2020-2021
The sentiment analysis domain has been deeply studied in the last few years, the analysis of social media content is still a challenging task due to the exponential growth of multimedia content. Natural language ambiguities and indirect sentiments within the social media text have made it hard to classify. Aspect-based sentiment analysis creates a need to develop explicit extraction techniques using syntactic parsers to exploit the relationship between the aspect and sentiment terms. Along with the extraction approaches, word embeddings are generated through Word2Vec models for the continuous low-dimensional vector representation of text that fails to capture the significant sentiment information. This paper presents a co-extraction model with refined word embeddings to exploit the dependency structures without using syntactic parsers. For this purpose, a deep learning-based multilayer dual-attention model is proposed to exploit the indirect relation between the aspect and opinion terms. In addition, word embeddings are refined by providing distinct vector representations to dissimilar sentiments, unlike the Word2Vec model. For this, we have employed a sentiment refinement technique for pre-trained word embedding model to overcome the problem of similar vector representations of opposite sentiments. The performance of the proposed model is evaluated on three benchmark datasets of SemEval Challenge 2014 and 2015. The experimental results indicate the effectiveness of our model compared to the existing state-of-the-art models for aspect-based sentiment analysis.
Research Grant by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), University of Jeddah, Jeddah, under research grant No. (UJ-12-18-DR), 2017-2018
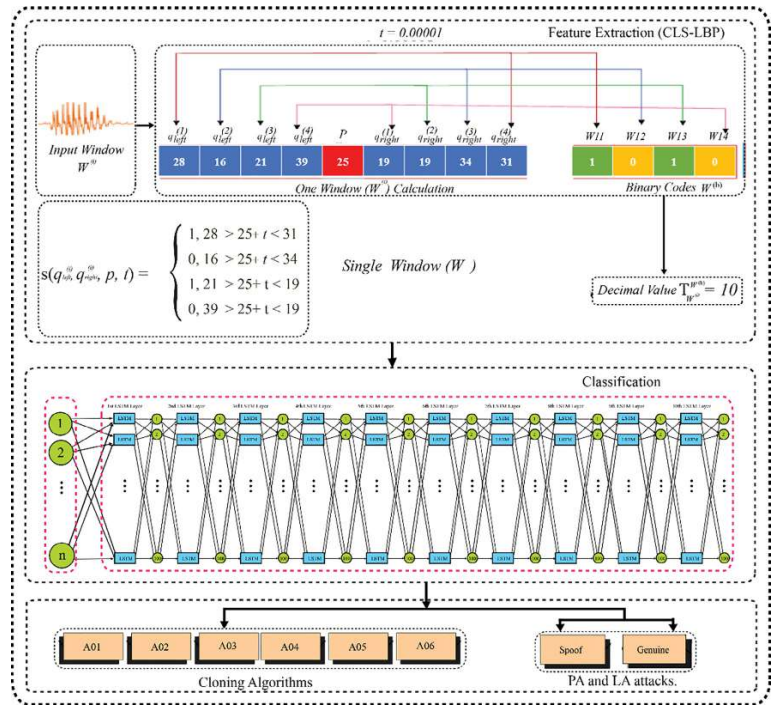
Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) systems are vulnerable to a variety of voice spoofing attacks, e.g., replays, speech synthesis, etc. The imposters/fraudsters often use different voice spoofing attacks to fool the ASV systems to achieve certain objectives, i.e., bypassing the security of someone’s home or stealing money from a bank account, etc. To counter such fraudulent activities on the ASV systems, we propose a robust voice spoofing detection system capable of effectively detecting multiple types of spoofing attacks. For this purpose, we propose a novel feature descriptor Center Lop-Sided Local Binary Patterns (CLS-LBP) for audio representation. CLS-LBP effectively analyzes the audios bidirectionally to better capture the artifacts of synthetic speech, microphone distortions of replay, and dynamic speech attributes of the bonafide signal. The proposed CLS-LBP features are used to train the long short-term memory (LSTM) network for detection of both the physical- (replay) and logical-access attacks (speech synthesis, voice conversion). We employed the LSTM due to its effectiveness to better process and learn the internal representation of sequential data. More specifically, we obtained an equal error rate (EER) value of 0.06% on logical-access (LA) while 0.58% on physical-access (PA) attacks. Additionally, the proposed system is also capable of detecting unseen voice spoofing attacks and also robust enough to classify among the cloning algorithms used to synthesize the speech. Performance evaluation on the ASVspoof 2019 corpus signify the effectiveness of the proposed system in terms of detecting the physical- and logical-access attacks over existing state-of-the-art voice spoofing detection systems.
Research Grant by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), University of Jeddah, Jeddah, under research grant No. (UJ-21-DR-28), 2020-2021
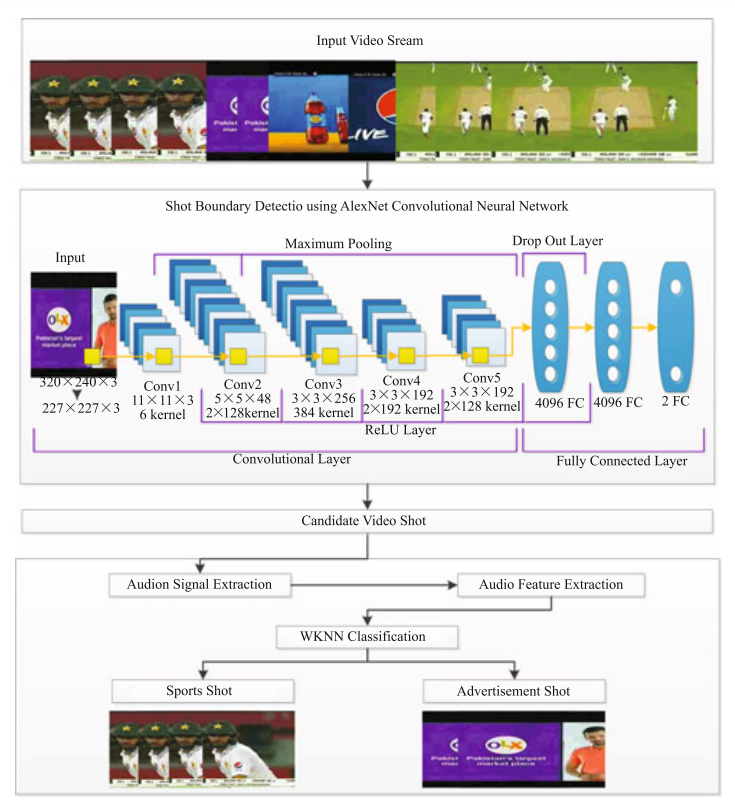
This work presents an effective two-step advertisement detection framework using audio-visual features. We employed AlexNet deep learning model for shot boundary detection to filter the candidate advertisement shots. Next, we represented the audio of the selected video shots through MFCC-GTCC spectral features-set to train the WKNN for advertisements detection and removal from the broadcasts. The average accuracy of 99.37% signify the effectiveness of the proposed framework. Performance of our method degrades to some extent under the conditions where audio tone of the advertisement and game shots become similar or if the advertisement contains no music in the background and sports contain musical tone.
Research Grant from Directorate ASR&TD UET, Award No. UET/ASR&TD/RG-1002-2, 2017-2018
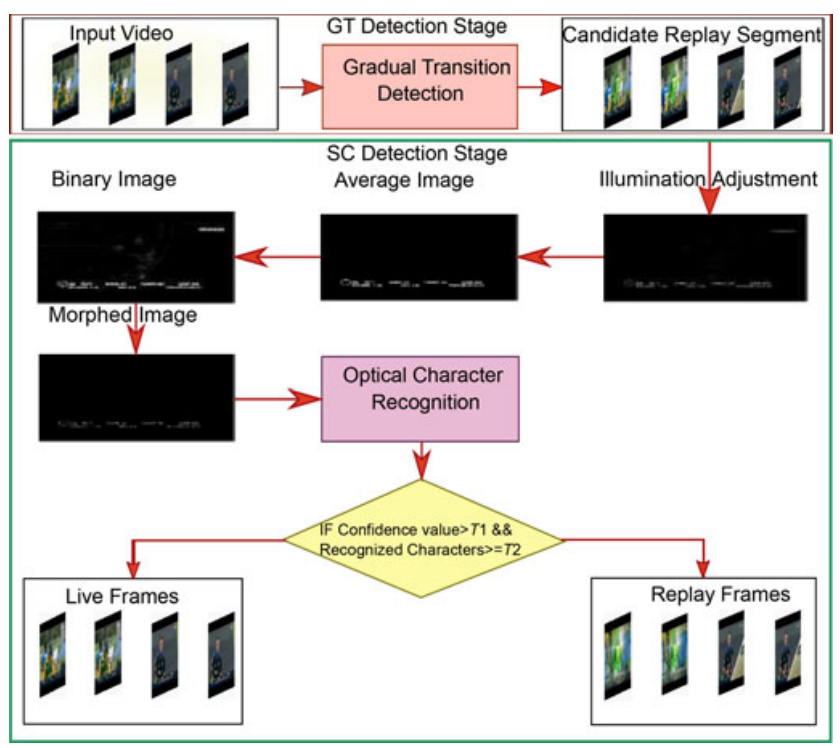
This letter presents a framework for replay detection in sports videos to generate highlights. For replay detection, the proposed work exploits the following facts: 1) broadcasters introduce gradual transition (GT) effect both at the start and at the end of a replay segment (RS), and 2) the absence of score captions (SCs) in an RS. The dual-threshold-based method is used to detect GT frames from the input video. A pair of successive GT frames is used to extract the candidate RSs. All frames in the selected segment are processed to detect SC. To this end, temporal running average is used to filter out temporal variations. First- and second-order statistics are used to binarize the running average image, which is fed to optical character recognition stage for character recognition. The absence/presence of SC is used for replay/live frame labeling. The SC detection stage complements the GT detection process, therefore, a combination of both is expected to result in superior computational complexity and detection accuracy. The performance of the proposed system is evaluated on 22 videos of four different sports (e.g., Cricket, tennis, baseball, and basketball). Experimental results indicate that the proposed method can achieve average detection accuracy ≥ 94.7%.
Research Grant from Directorate ASR&TD UET Taxila, Award No. UET/ASR&TD/RG-1002-3, 2017-2018
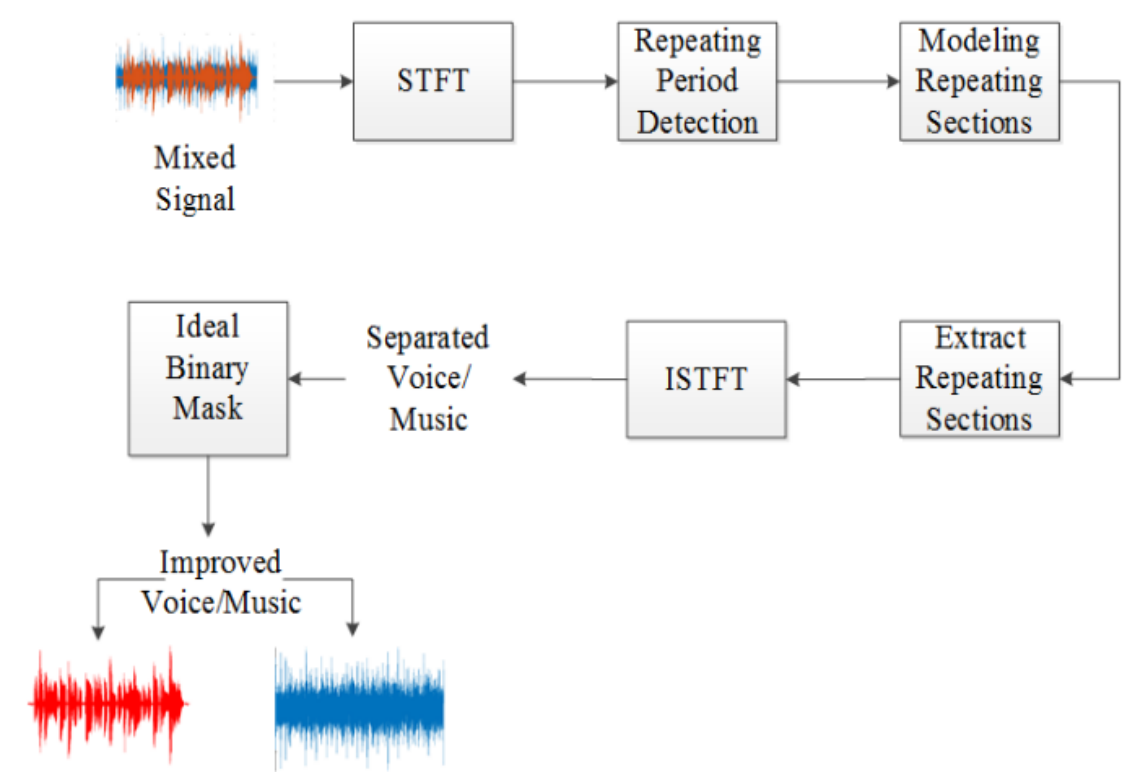
Speech and music segregation from a single channel is a challenging task due to background interference and intermingled signals of voice and music channels. It is of immense importance due to its utility in wide range of applications such as music information retrieval, singer identification, lyrics recognition and alignment. This paper presents an effective method for speech and music segregation. Considering the repeating nature of music, we first detect the local repeating structures in the signal using a locally defined window for each segment. After detecting the repeating structure, we extract them and perform separation using a soft time-frequency mask. We apply an ideal binary mask to enhance the speech and music intelligibility. We evaluated the proposed method on the mixtures set at-5 dB, 0 dB, 5 dB from Multimedia Information Retrieval-1000 clips (MIR-1K) dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method for speech and music segregation outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of Global-Normalized-Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (GNSDR) values.
Research Grant from Directorate ASR&TD UET Taxila, Award No. UET/ASR&TD/RG-1002-4, 2017-2018
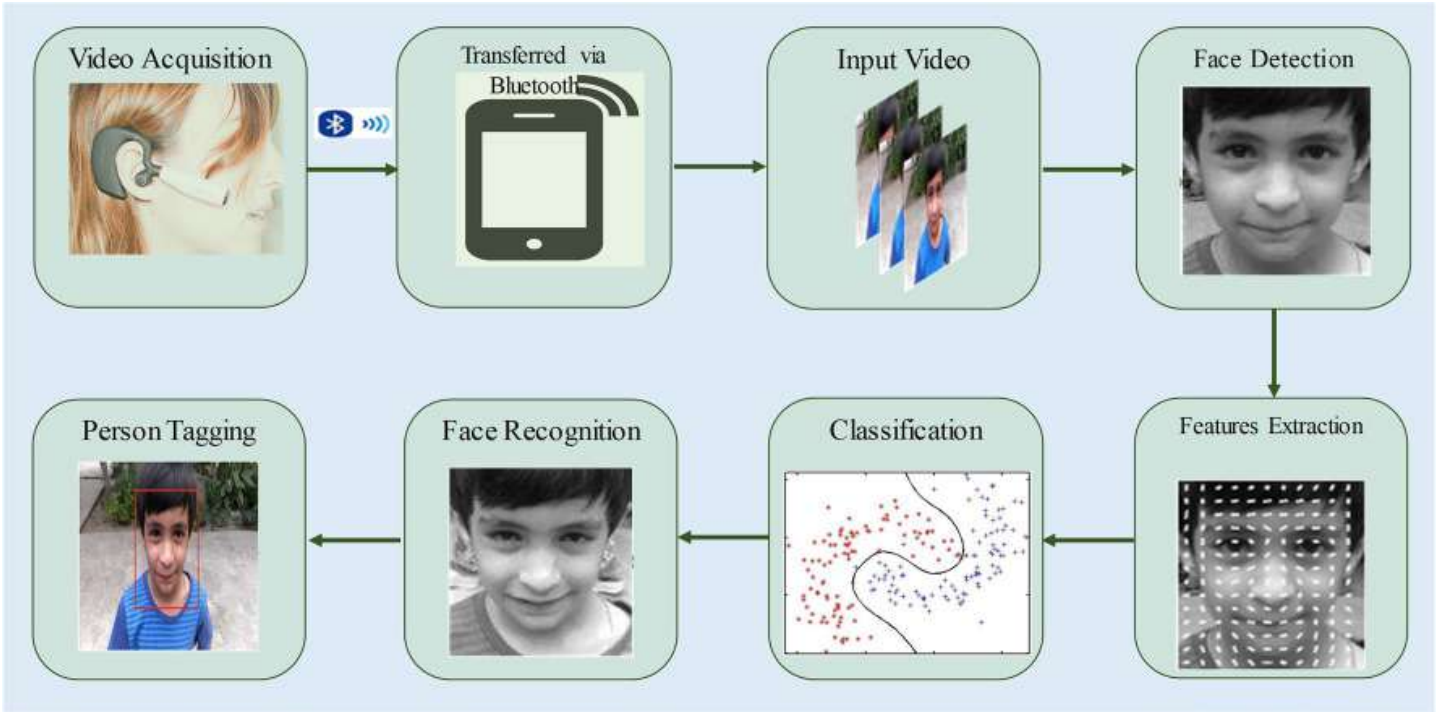
Alzheimer patients face difficulty to remember the identity of persons and performing daily life activities. This paper presents a hybrid method to generate the egocentric video summary of important people, objects and medicines to facilitate the Alzheimer patients to recall their deserted memories. Lifelogging video data analysis is used to recall the human memory; however, the massive amount of lifelogging data makes it a challenging task to select the most relevant content to educate the Alzheimer’s patient. To address the challenges associated with massive lifelogging content, static video summarization approach is applied to select the key-frames that are more relevant in the context of recalling the deserted memories of the Alzheimer patients. This paper consists of three main modules that are face, object, and medicine recognition. Histogram of oriented gradient features are used to train the multi-class SVM for face recognition. SURF descriptors are employed to extract the features from the input video frames that are then used to find the corresponding points between the objects in the input video and the reference objects stored in the database. Morphological operators are applied followed by the optical character recognition to recognize and tag the medicines for Alzheimer patients. The performance of the proposed system is evaluated on 18 real-world homemade videos. Experimental results signify the effectiveness of the proposed system in terms of providing the most relevant content to enhance the memory of Alzheimer patients.
Research Grant from Directorate ASR&TD UET Taxila, Award No. UET/ASR&TD/RG-1002-5, 2017-2018.
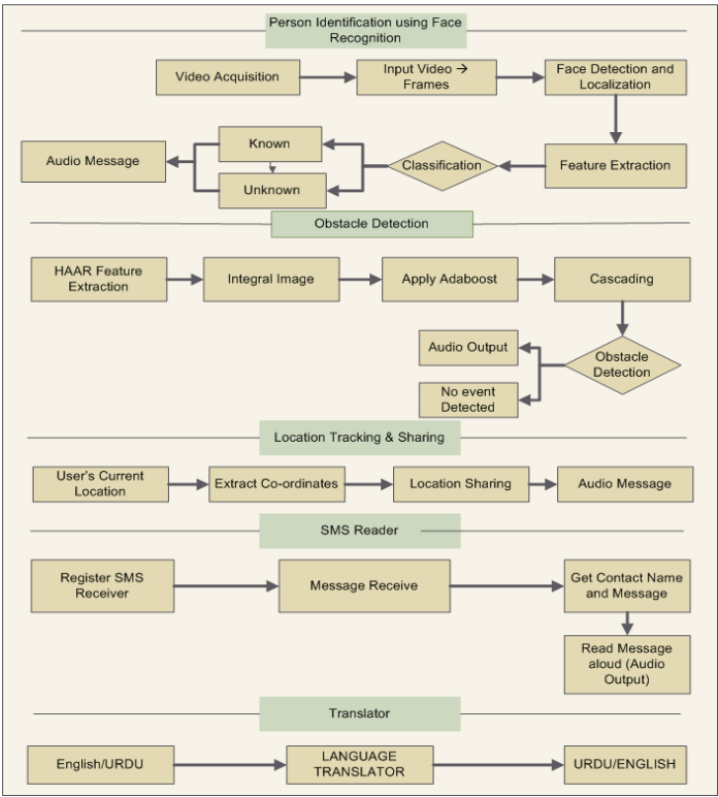
This paper presents an effective method of providing day-to-day mobility aid to visually impaired people. An android application named X-EYE using LOOXCIE wearable camera is designed for blind people to navigate safely. Existing navigation aid systems use various hardware components such as sensors that are expensive and cause health hazards. The proposed system presents an economical solution using a wearable camera and a smart phone to provide safe navigation facility to the visually impaired user. X-EYE provides the features of obstacle detection, person recognition, location tracking and sharing, SMS reader, and language translation. Audio messages are specifically generated to provide better usability to the blind/visually impaired user. The proposed system is robust to egocentric video limitations i.e. partial appearance of objects, sudden background change, jitter effects, and illumination conditions. Performance of the proposed method is evaluated on ten real-time egocentric videos. Experimental results indicate the effectiveness of our method in terms of providing safe mobility services to visually impaired people.
Research Grant from Ignite, 2019-2020